Shareholders’ equity includes preferred stock, common stock, retained earnings, and accumulated other comprehensive income. Current assets are those that can be converted to cash within a year, such as accounts receivable and inventory. Long-term assets are those that cannot be converted to cash or consumed within a year, such as real estate properties, manufacturing plants, equipment, https://www.kelleysbookkeeping.com/ and intangible items like patents. As discussed above, it can also be calculated by adding share capital to retained earnings. For starters, shareholder equity tells you the total return on investment versus the amount invested by equity investors. If a small business owner is only concerned with money coming in and going out, they may overlook the statement of stockholders’ equity.
Retained Earnings
Mr. Arora is an experienced private equity investment professional, with experience working across multiple markets. Rohan has a focus in particular on consumer and business services transactions time period assumption and operational growth. Rohan has also worked at Evercore, where he also spent time in private equity advisory. However, the effect of dividends varies based on the type of dividends issued.
Get Your Business a One-Year Sam’s Club Membership for Just $14
Paid-in capital can rise when a company issues new shares or sells treasury shares at a price higher than their par value, increasing paid-in capital and stockholders’ equity. This is the other formula, where share capital, retained earnings, and treasury stock are needed to formulate owner’s equity. A balance sheet can’t predict changes in the value of a company’s assets or changes to its liabilities that haven’t occurred yet.
Role of Stockholders’ Equity in Decision-Making
It is the difference between shares offered for subscription and outstanding shares of a company. In most cases, retained earnings are the largest component of stockholders’ equity. This is especially true when dealing with companies that have been in business for many years. During a liquidation process, the value of physical assets is reduced and there are other extraordinary conditions that make the two numbers incompatible. Retained earnings should not be confused with cash or other liquid assets. The retained earnings are used primarily for the expenses of doing business and for the expansion of the business.
Common Stock and Additional Paid-In Capital (APIC)
Current liabilities are debts that are due for repayment within one year, such as accounts payable and taxes payable. Long-term liabilities are obligations that are due for repayment in periods beyond one year, including bonds payable, leases, and pension obligations. You can use several years of retained earnings for assets, expenses or other purposes to grow a business. Positive shareholders’ equity means a company has enough assets to cover its debts or liabilities. Negative shareholders’ equity, on the other hand, means that the liabilities of a firm exceed its total asset value. A statement of shareholder equity is a section of the balance sheet that reflects the changes in the value of the business to shareholders from the beginning to the end of an accounting period.
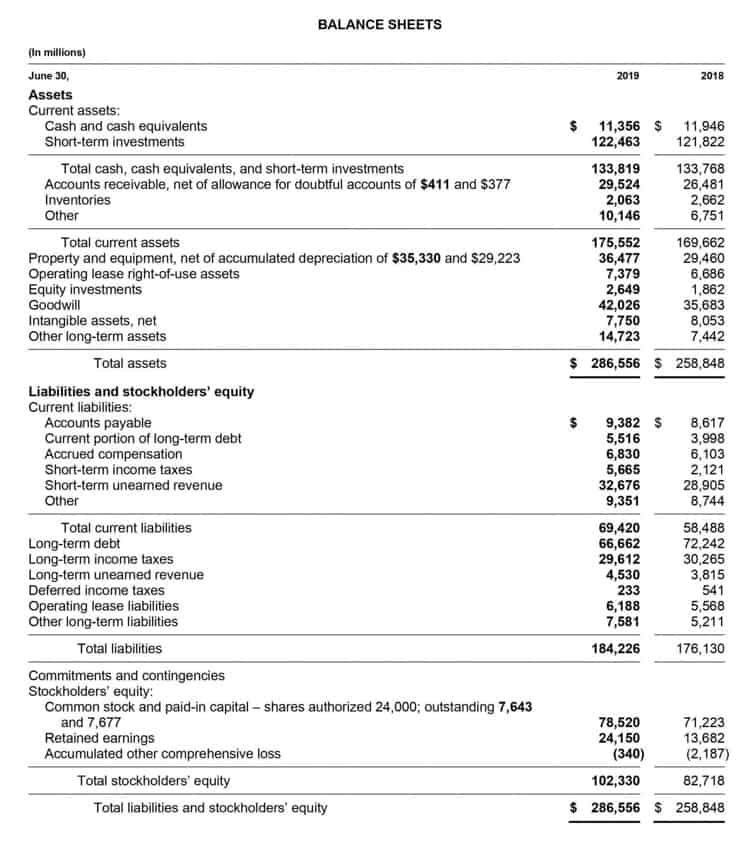
To calculate, you first need to find out your target company’s total assets and total liabilities. Total assets includes all long-term and current assets such as plant, machinery, property, inventory, cash on hand and receivables owned by the company. Total assets must equal the total liabilities and stockholders equity in order for the balance sheet to balance. Shareholders equity is also known as owners’ equity, net worth, owner’s capital and simply equity. Many investors look at companies with negative shareholder equity as risky investments.
Increases or decreases on either side could shift the needle substantially when it comes to the direction in which stockholders’ equity moves. Return on equity is a measure that analysts https://www.kelleysbookkeeping.com/accumulated-depreciation-and-depreciation-expense/ use to determine how effectively a company uses equity to generate a profit. It is obtained by taking the net income of the business divided by the shareholders’ equity.
- Liability represents the total debt of the company and owner’s capital represents shareholders’ ownership.
- As a result, financial experts consider a firm’s retained earnings and its owner’s equity when analyzing its financial soundness.
- Investors, lenders and analysts use stockholders’ equity to inform their investment and lending decisions regarding a company.
- Net income is the total revenue minus expenses and taxes that a company generates during a specific period.
- Stockholders’ equity can be a key indicator of a company’s stability, growth potential and ability to attract investments.
Owner’s equity may rise as a result of selling stock, increasing revenues, cutting operational expenditures, etc. The benefit is that there are no interest payments or requirements to return the investment. Instead, the current market value of each share must be considered, which is usually more than the nominal value.
More technically, it’s the value of an asset, like property, minus its liabilities, like debt. Shareholder equity influences the return generated concerning the total amount invested by equity investors. This is because years of retained earnings could be used for expenses or any asset to help the business grow. Bonds are contractual liabilities with guaranteed annual payments unless the issuer defaults, whereas dividend payments from stock ownership are discretionary and not fixed. We can apply this knowledge to our personal investment decisions by keeping various debt and equity instruments in mind. Although the level of risk influences many investment decisions we are willing to take, we cannot ignore all the critical components discussed above.